Greek alphabet (Ελληνικό αλφάβητο)
Origin
The Greek alphabet has been in continuous use for the past 2,750 years or so since about 750 BC. It was developed from the Canaanite/Phoenician alphabet and the order and names of the letters are derived from Phoenician. The original Canaanite meanings of the letter names was lost when the alphabet was adapted for Greek. For example, alphacomes for the Canaanite aleph (ox) and beta from beth (house).
At first, there were a number of different versions of the alphabet used in various different Greek cities. These local alphabets, known as epichoric, can be divided into three groups: green, blue and red. The blue group developed into the modern Greek alphabet, while the red group developed into the Etruscan alphabet, other alphabets of ancient Italy and eventually the Latin alphabet.
By the early 4th century BC, the epichoric alphabets were replaced by the eastern Ionic alphabet. The capital letters of the modern Greek alphabet are almost identical to those of the Ionic alphabet. The minuscule or lower case letters first appeared sometime after 800 AD and developed from the Byzantine minuscule script, which developed from cursive writing.
Notable features
- Type of writing system: alphabet - the first one to include vowels.
- Direction of writing: Originally written horizontal lines either from right to left or alternating from right to left and left to right (boustrophedon/βουστροφηδόν). Around 500 BC the direction of writing changed to horizontal lines running from left to right.
- Diacritics to represent stress and breathings were added to the alphabet in around 200 BC. In 1982 the diacritics representing breathings, which were not widely used after 1976, were officially abolished by presidential decree.
- The letter sigma has a special form which is used when it appears at the end of a word.
Used to write
Greek (Ελληνικά), an Indo-European language spoken by about 14 million people mainly in Greece and Cyprus, where it is an official language. Greek is also recognised as a minority language in parts of Turkey, Italy and Albania.
Today the Greek alphabet is used only to write Greek, however at various times in the past it has been used to write such languages as Lydian, Phrygian, Thracian, Gaulish, Hebrew, Arabic, Old Ossetic, Albanian, Turkish, Aromanian, Gagauz, Surguch and Urum.
Greek alphabet - Classical Attic pronunciation

Note
- Σ = [z] before voiced consonants
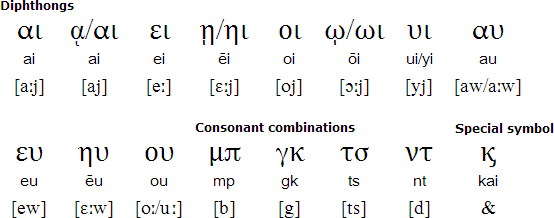
Greek alphabet - Modern pronunciation




![]() Books on the Greek alphabet and the Greek language
Books on the Greek alphabet and the Greek language
Corrections and notes on pronunciation provided by Dimitris Christoulias (Δημήτρης Χριστούλιας)
Links
Information about the Greek language
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greek_language
Free Greek fonts
http://www.phantis.com/customer.service/greek.fonts.html
http://www.ntgateway.com/greek/fonts.htm
http://www.hellenic.net/fonts
http://www.biblicalgreek.org/links/fonts.html
Online Greek lessons
http://www.kypros.org/LearnGreek/ (Modern/Ancient)
http://www.ilearngreek.com (Modern)
http://www.greece.org/gr-lessons/ (Modern)
http://www.xanthi.ilsp.gr/filog/ (Modern)
http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Modern_Greek (Modern)
http://greekthrumusic.blogspot.com/ (Modern)
http://www.ibiblio.org/koine/greek/lessons/ (New Testament)
http://socrates.berkeley.edu/~ancgreek/ (Ancient)
http://www.textkit.com (Ancient)
Greek language resources, including dictionaries, grammar and useful phrases
http://www.greek-language.org
Greek learner forum
http://z13.invisionfree.com/greek_learner_forum/
Greek transliteration and spell check
http://gr.translit.cc/
Online Greek-English dictionary
http://www.kypros.org/cgi-bin/lexicon/
Greek Electronic talking dictionaries
http://www.ectaco.com
Greek Language and Linguistics
http://greek-language.com
Information about Greek personal names
http://www.behindthename.com/nmc/gre-anci.php
http://www.lgpn.ox.ac.uk




댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기